Why Arrays?
- Store lists of data (grades, sensor readings).
- Form the base for matrices, strings, vectors.
- Efficient: direct access via index.
- Easily processed using loops.
Accessing elements!!

Historical Perspective
Early memory (1950s–70s) used Magnetic Core Memory: tiny rings storing bits in a physical grid.
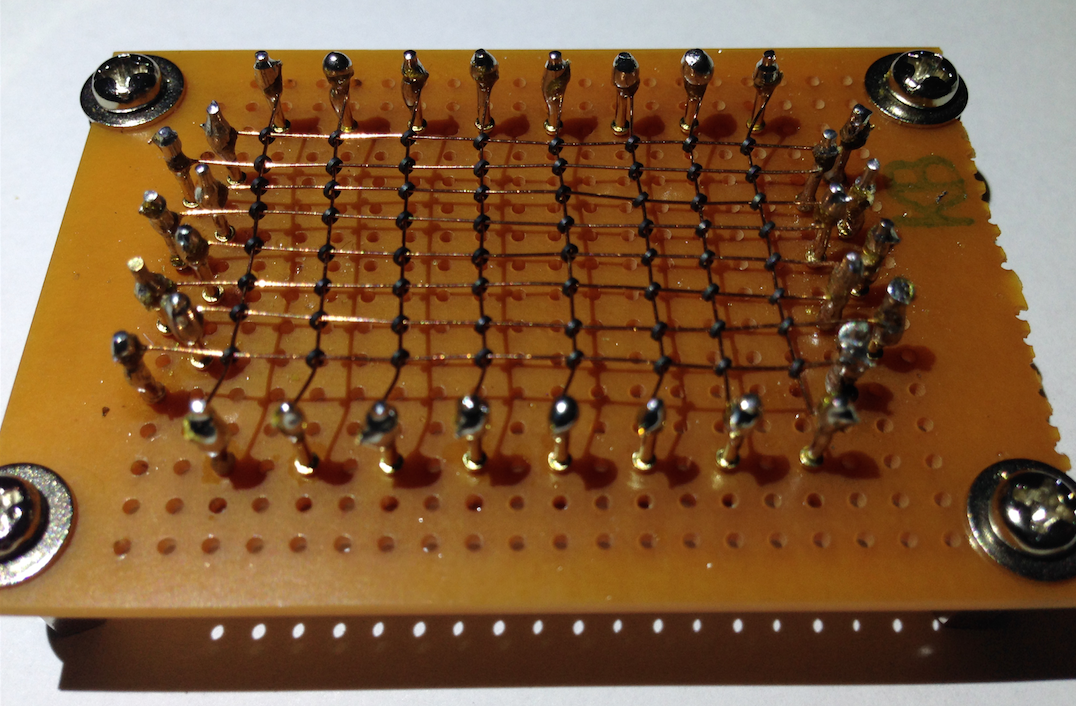
Its [row][col] access directly inspired array indexing.
Accessing arr[5] in a 5-element array...

Undefined behavior: your new superpower.
Summary
- Arrays store fixed-size collections.
- Zero-based indexing: arr[0] is first.
- Loops are natural with arrays.
- Beware out-of-bounds errors.
- Prefer `std::vector` in modern C++.
Back to Course Outline
Back to Course OutlinePrevious: Lecture 5 | Next: Lecture 7